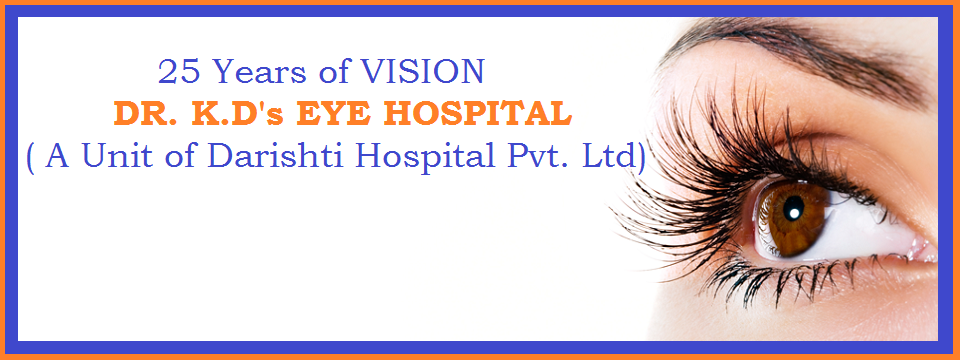
PHACO SURGERY(Phacoemulsification)
Phacoemulsification refers to modern cataract surgery in which the eye's internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic hand-piece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution, thus maintaining the anterior chamber, as well as cooling the hand-piece. Being a delicate organ, the eye requires extreme care before, during and after a surgical procedure. An ophthalmologist must diagnose a cataract and conduct or supervise the operation. Proper anesthesia is a must for ocular surgery. Topical anesthesia is most commonly employed, typically by the instillation of a local anesthetic such as tetracaine or lidocaine. Alternatively, lidocaine and/or longer-acting bupivacaine anesthestic may be injected into the area surrounding (peribulbar block) or behind (retrobulbar block) the eye muscle cone to more fully immobilize the extraocular muscles and minimize pain sensation. A facial nerve block using lidocaine and bupivacaine may occasionally be performed to reduce lid squeezing. General anesthesia is recommended for children, traumatic eye injuries with cataract, for very apprehensive or uncooperative patients and animals. Cardiovascular monitoring is preferable in local anesthesia and is mandatory in the setting of general anesthesia. Proper sterile precautions are taken to prepare the area for surgery, including use of antiseptics like povidone-iodine. Sterile drapes, gowns and gloves are employed. A plastic sheet with a receptacle helps collect the fluids during phacoemulsification.
Benefits of Phaco surgery:
> No hospitalization - Walk in, Walk out surgery.
> Early visual rehabilitation.
> Lesser induced astigmatism because of smaller incision.
> No bandages minimal precautions.
> No restriction on normal activities. Can join work from next morning.
> Fast recovery of good vision in a matter of days.
> Final spectacles at one or two weeks.
> Smaller incision- hence lesser complications related to the incision size.